
Enterprise Security user interface
Download and install the CheckPoint SmartConsole Rxx.zz GUI firewall rule set and log reporting application from https://partnergate.sonera.com/enterprisesecurity.html. Behind the link you will also find the installation instructions under “Rule and tracking applications installation instructions.”
Log-in and use of the user interface view
After the installation is complete, you can log into the user interface view of the SmartDashboard application.
Enter the IP address of the SmartDashboard server and the username and password you got in connection with the delivery into the SmartDashboard login window. The IP address of the SmartDashboard user interface can also be found in the connection details listed in SurfManager.
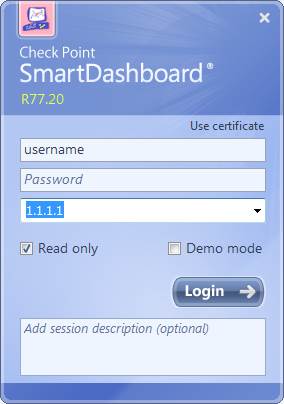
Figure. SmartDashboard login.
The overview appears.
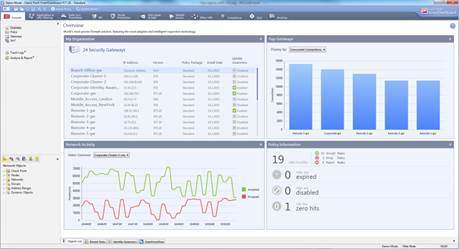
Figure. Overview of the SmartDashboard.
The options listed on the top of the SmartDashboard are links to the different services (firewall, application and bandwidth management, etc.). The services are listed in a table. Click on a service to see service overview and viewing instructions.
Services
2 Network address
translation (NAT)
3 Application and
bandwidth control and Web filtering
3.1 Application and
bandwidth control and Web filtering rule
3.2 Application and
bandwidth control and Web filtering user messages
4 Antivirus, botnet
protection and advanced threat protection
4.1 Antivirus,
botnet protection and advanced threat protection rule
4.2 Antivirus,
botnet protection and advanced threat protection profile
4.3 Antivirus,
botnet protection and advanced threat protection user message
5.1 Intrusion
prevention profile
5.2 Intrusion
prevention geographical protection
1 Firewall
Firewall rules filter traffic between two networks, for example the company’s LAN or subscriber line and the Internet, as specified in the firewall rules.
The firewall rules can be seen select Firewall->Policy
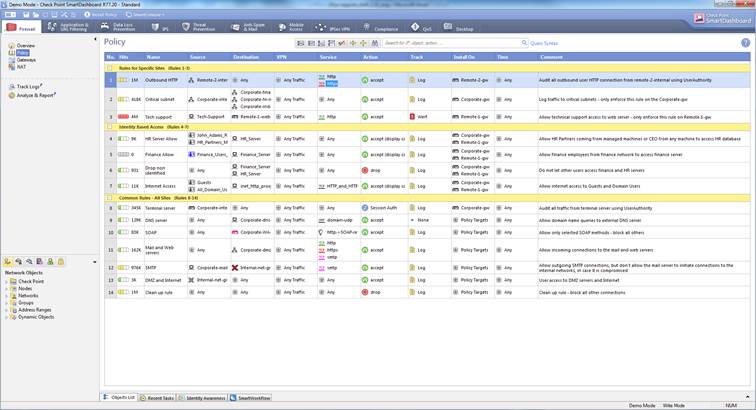
Figure. Firewall rules
In the following, you will find a picture of a firewall rule and descriptions of the rule settings.
![]()
Figure: Firewall rule.
Rule number (No.)
The rule number specifies the point in the rule base where the rule is read. The firewall checks the rule base against the connection details in sequential order and stops when it finds a match. For this reason, the rule numbers are important.
Hits
Hits counter inform how many times this rule have to use at a specific time period.
Rule name (Name)
The name will remain unchanged in the rule base.
Source
The source address can be an individual IP address, an IP network address, an object group including several IP addresses, IP networks or groups, and users or user groups or devices or device groups obtained from a user directory.
Destination
Service
The TCP/UDP port(s), service(s) and group(s) to be used are specified in the service.
Action
The following options are available when the action is specified:
· Accept, i.e. accept the traffic.
· Reject, i.e. reject the traffic. This differs from Drop in that the firewall informs the party attempting to establish a connection about the disconnection.
· Drop, i.e. drop traffic.
Log
Specify whether the rule in question is to be tracked.
Time
Specify when the rule is valid. If the time is not specified, the rule is always valid. Here you can specify, for example, that the rule is valid only on weekdays. The available options are:
When the rule is activated or when the rule expires. E.g. activated 31-1-2015-08:00 and expires 31-12-2015-16:00.
The validity of the rule is restricted to a certain period of time or certain weekdays or certain days of the month. E.g. the rule is valid 08:00-16:00 Monday-Friday.
The comment is a free text attached to a rule.
Return change targets table
2 Network address translation (NAT)
NAT (network address translation) rules specify which addresses or services are to be translated into which addresses or services. The rules are similar to those used in a standard rule base to specify the traffic to be allowed or blocked.
The network address translation rules can be seen select Firewall->NAT
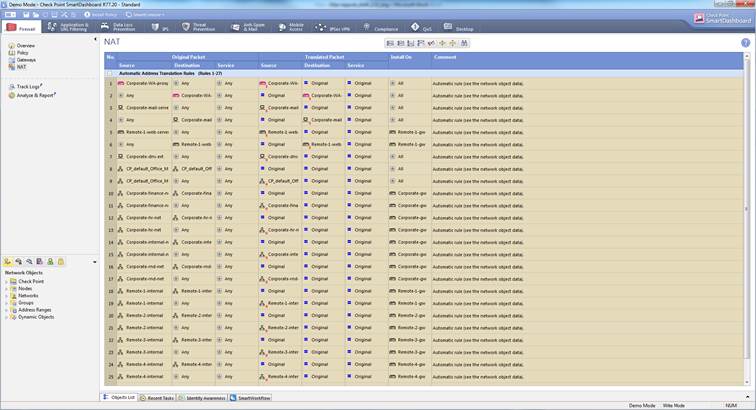
Figure: NAT rules
In the following, you will find a picture of a NAT rule and descriptions of the rule settings.

Figure: NAT rule
Rule number (No.)
The rule number defines the point in the rule base where the rule is read. The security device checks the rule base against the connection details in sequential order and stops when it finds a match. For this reason, the rule numbers are important.
Original packet source
The original source address used. It can be an individual IP address, an IP network, or an object group including several IP addresses, IP networks or groups.
Original packet destination
The original destination address used. It can be an individual IP address, an IP network or an object group including several IP addresses, networks or groups.
Original packet service
The TCP/UDP port, service or group to be used are specified in the service.
Translated packet source
The translated source address. It can be an individual IP address, an IP network, or an object group including several IP addresses, IP networks or groups.
Translated packet destination
The translated destination address. It can be an individual IP address, an IP network or an object group including several IP addresses, networks or groups.
Translated packet service
The translated TCP/UDP port or service.
Comment
The comment is a free text attached to a rule.
Return change targets table
3 Application and bandwidth control and Web filtering
Application and bandwidth control functionality allows network use to be identified, allowed, prevented or limited application-specifically. Typical services to be identified are social media applications, video services and file sharing services. The technology identifies thousands of different applications and their sub-applications. This functionality allows users to be informed in real time of application use limitations, the risks of the Internet, and the security policy of the organization.
In web content filtering, the URL (Uniform Resource Locator) of a downloaded Internet page is compared with a database where web pages are pre-categorized into certain page categories. This functionality allows users to be informed in real time of web traffic restrictions, the risks of the Internet, and the security policy of the organization.
The Application and bandwidth control and Web filtering can be seen select Application&URL Filtering->Policy
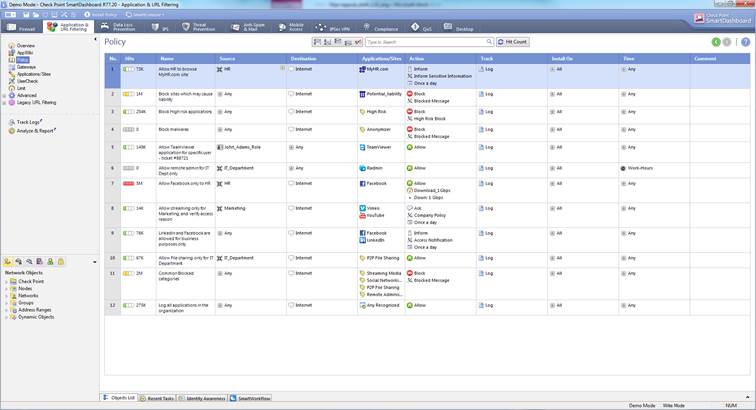
Figure: Application and bandwidth control and Web filtering rules
3.1 Application and bandwidth control and
Web filtering rule
In the following, you will find a picture of a application and bandwidth control rule as well as Web filtering rule and descriptions of the rule settings.
![]()
Figure: Application and bandwidth rule.
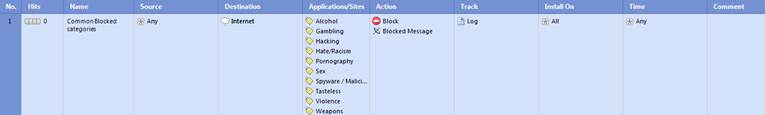
Figure: Web filtering rule.
Rule number (No.)
The rule number defines the point where the rule is read.
Rule name (Name)
The name will remain unchanged in the rule base. The name can include up to 30 characters.
Hits
Hits counter inform how many times this rule have to use at a specific time period.
Source
The source can be an individual IP address, an IP network, a user / user group or an object group including several IP addresses, IP networks, users or groups.
Destination
The destination can be an individual IP address, an IP network or an object group including several IP addresses, networks or groups.
Application category or application (Applications/Sites)
Specify the application or category used. You can view the applications, categories and risk classification by selecting AppWiki in the GUI client. To view all applications, select “Include Social Network Widgets”.
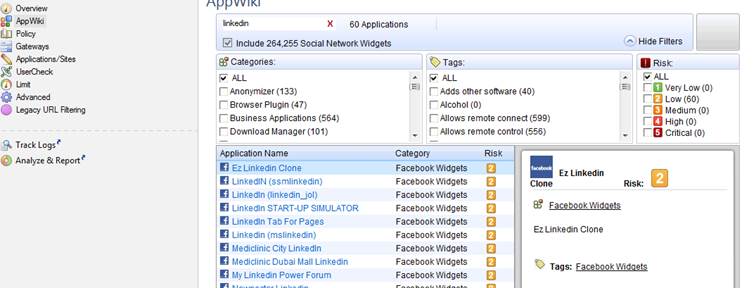
Figure: AppWiki display with “linkedin” as the search criterion
Below table, where specified belongs category application and bandwidth control category, web filtering category or both categories.
|
Application |
Web filtering |
Application and web filtering |
|
Adds other software |
Alcohol |
Anonymizer |
|
Allows remote connect |
Art / Culture |
Blogs / Personal Pages |
|
Allows remote control |
Botnets |
|
|
Autostarts/Stays Resident |
Business / Economy |
File Storage and Sharing |
|
BitTorrent protocol |
Computers / Internet |
Games |
|
Browser Plugin |
Education |
Instant Chat |
|
Bundles Software |
Entertainment |
Media Sharing |
|
Business Applications |
Fashion |
P2P File Sharing |
|
Content Provider and Sharing |
Financial Services |
Search Engines / Portals |
|
Critical Risk |
Gambling |
Social Networking |
|
Download Manager |
General |
Web Advertisements |
|
eDonkey |
Government / Military |
|
|
|
Greeting Cards |
|
|
Encrypts communications |
Hacking |
|
|
Facebook Business |
Hate / Racism |
|
|
Facebook Education |
Health |
|
|
Facebook Entertainment |
Illegal / Questionable |
|
|
Facebook File Sharing |
Illegal Drugs |
|
|
Facebook Friends & Family |
Inactive Sites |
|
|
Facebook Games |
Job Search / Careers |
|
|
Facebook Lifestyle |
Media Streams |
|
|
Facebook Popular |
Nature / Conservation |
|
|
Facebook Sports |
News / Media |
|
|
Facebook Utilities |
Newsgroups / Forums |
|
|
Facebook Widgets |
Non-profits & NGOs |
|
|
Friendster Widgets |
Nudity |
|
|
FTP Protocol |
Orkut Games |
|
|
Games |
Personals / Dating |
|
|
Gnutella protocol |
Phishing |
|
|
Google Talk protocol |
Political / Legal |
|
|
High Bandwidth |
Pornography |
|
|
High Risk |
Real Estate |
|
|
IM Aggregator |
Recreation |
|
|
Instant Messaging |
Religion |
|
|
IPTV |
Restaurants / Dining / Food |
|
|
IRC protocol |
Sex |
|
|
Jabber protocol |
Sex Education |
|
|
LinkedIn Widgets |
Shopping |
|
|
Linux Installer |
Software Downloads |
|
|
Logs e-mail |
Spam |
|
|
Logs IM |
Sports |
|
|
Low Risk |
Spyware / Malicious Sites |
|
|
Mac Installer |
Tasteless |
|
|
Meduim Risk |
Translation |
|
|
Micro blogging |
Travel |
|
|
Mobile Software |
Uncategorized |
|
|
MySpace Entertainment |
Weapons |
|
|
MySpace Games |
Vehicles |
|
|
MySpace Lifestyle |
Violence |
|
|
MySpace Popular |
||
|
MySpace Sports |
||
|
MySpace Utilities |
||
|
MySpace Widgets |
||
|
Network Protocols |
||
|
Network Utilities |
||
|
Ning.com Widgets |
||
|
Opens ports |
||
|
Orkut Entertainment |
||
|
Orkut Lifestyle |
||
|
Orkut Popular |
||
|
Orkut Sports |
||
|
Orkut Utilities |
||
|
Orkut Widgets |
||
|
Oscar protocol |
||
|
Port agility |
||
|
Remote Administration |
||
|
SCADA Protocols |
||
|
Search Engines / Portals |
||
|
Sends mail |
||
|
Share Files |
||
|
Share links |
||
|
Share Music |
||
|
Share photos |
||
|
Share videos |
||
|
SMS Tools |
||
|
Social Networking |
||
|
Social Plugins |
||
|
Software Update |
||
|
SSL Protocol |
||
|
Stealth Tactics |
||
|
Streaming Media Protocols |
||
|
Supports File Transfer |
||
|
Supports IM |
||
|
Supports Streaming |
||
|
Supports video/webcam |
||
|
Supports VoIP |
||
|
Torrent Trackers |
||
|
Transmits Information |
||
|
Tunnels |
||
|
Twitter Clients |
||
|
UDP Protocol |
||
|
Unknown Traffic |
||
|
Used for Web-Based Support |
||
|
Very Low Risk |
||
|
Web Advertisements |
||
|
Web Based Instant Messaging |
||
|
Web Browser |
||
|
Web Conferencing |
||
|
Web Content Aggregators |
||
|
Web Desktop |
||
|
Web Services Provider |
||
|
Web Spider |
||
|
Video Conferencing |
||
|
Windows Messenger protocol |
||
|
Virtual Worlds |
||
|
Voice Mail |
||
|
VoIP |
||
|
Yahoo Messenger protocol |
||
|
VoIP |
||
|
Yahoo Messenger protocol |
Figure. Application and bandwidth control and web filtering categories (Update 21.7.2015)
Action
The action is specified using one of the following options:
· Block the traffic: A user can be notified of traffic blocking by means of a user message. The user message specifying here.
· Allow the traffic: The frequency band of allowed traffic can also be limited (Limit).
· Inform: This means that the traffic is allowed, but the user is informed of the terms and conditions of use. The user message is specified separately. If necessary, it is possible to specify how often the user message is shown to the user (once a day, once a week, once a month; the shortest interval available is once an hour). The frequency band of the traffic can also be limited (Limit).
· Ask: This means that the traffic is allowed, but the user is informed of the terms and conditions of use and requested to confirm the opening of the connection. The user message is specified separately. If necessary, it is possible to specify how often the message is shown to the user (once a day, once a week, once a month; the shortest interval available is once an hour). The frequency band of the traffic can also be limited (Limit).
Track
Specify whether the rule in question is to be tracked.
Time of validity of the rule (Time)
If the time is not specified, the rule is always valid. Here you can specify, for example, that the rule is valid only on weekdays. The available options are:
When the rule is activated or when the rule expires. E.g. activated 31-1-2015-08:00 and expires 31-12-2015-16:00.
The validity of the rule is limited to a certain period of time or certain weekdays or certain days of the month. E.g. the rule is valid 08:00-16:00 Monday-Friday.
Comment
The comment is a free text attached to a rule.
3.2 Application and bandwidth control and Web filtering user messages
User messages makes possible to be informed in real time of organisation security policy.
The Application and bandwidth control and Web filtering user message can be seen select Application&URL Filtering->User Check. Message content can see in browser to select “Preview in browser”
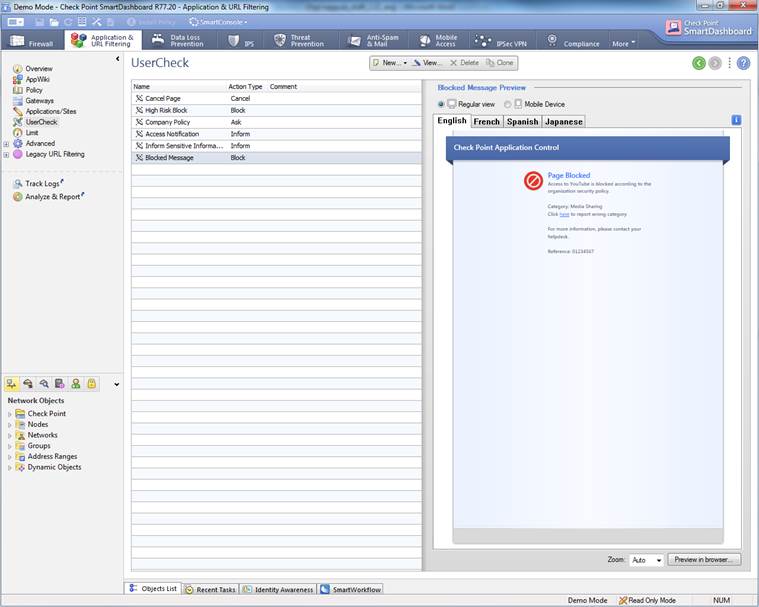
Figure. User message
In the following, you will find a picture of the user message (Block) of Application and bandwidth control and Web filtering and how it is shown in the browser, and also descriptions of the settings that can be made in the fields.
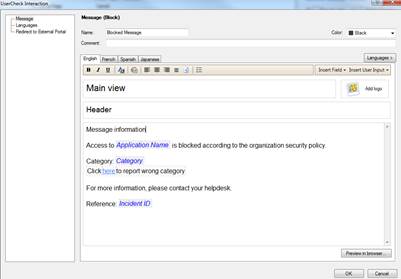
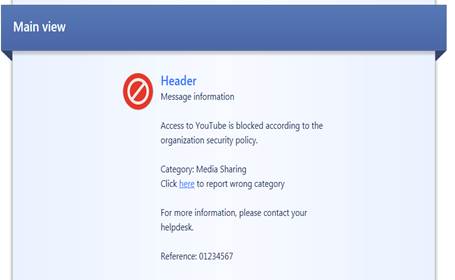
Figure: User message definition.
Message type (Block/Ask/Inform)
The message can be a block, inform or ask message. A block message is sent, if the traffic is not allowed. An inform message is sent to inform the user, who then selects either OK or Cancel. An ask message requests the user to confirm whether he or she approves the terms and conditions of use.
Message name (Name)
Specify a name for the message. The name is not shown in the user message.
Message comment (Comment)
Specify a comment for the message. The comment is not shown in the user message.
User message main view (Main view)
Specify the main view (main heading) to be shown on top of the user message.
User message logo
Specify the logo to be shown in the user messages.
User message header (Header)
Specify a header for the user message information field.
User message information (Message information)
Specify the contents of the user message.
Return change targets table
4 Antivirus, botnet protection and
advanced threat protection
The antivirus service scans the files downloaded through the firewall and prevents any malware from entering the customer network according to the company’s scanning policy. The antivirus service supports the most common web browsing, data transmission and email protocols. The user is notified of any viruses detected. The firewall updates the virus database automatically from the manufacturer’s update servers. Typically there is no need to make any changes to the rule base and the profile, but the protection is sufficient if the default values are used.
Botnet malware allows criminals to manage workstations and servers remotely and to perform unauthorized actions – such as steal data, distribute spam and spread malware – and to force them to participate in DoS attacks.
This functionality allows botnet-contaminated workstations and servers to be identified and traffic from them to botnet management servers to be prevented. It helps you to minimize damage by preventing for instance the transmission of confidential information from the company's network.
The Advanced Threat Protection service monitors how a file behaves in a workstation environment and strives to prevent unknown malware from entering the customer network.
The Antivirus, botnet protection and advanced threat protection can be seen select Threat Prevention -> Policy.
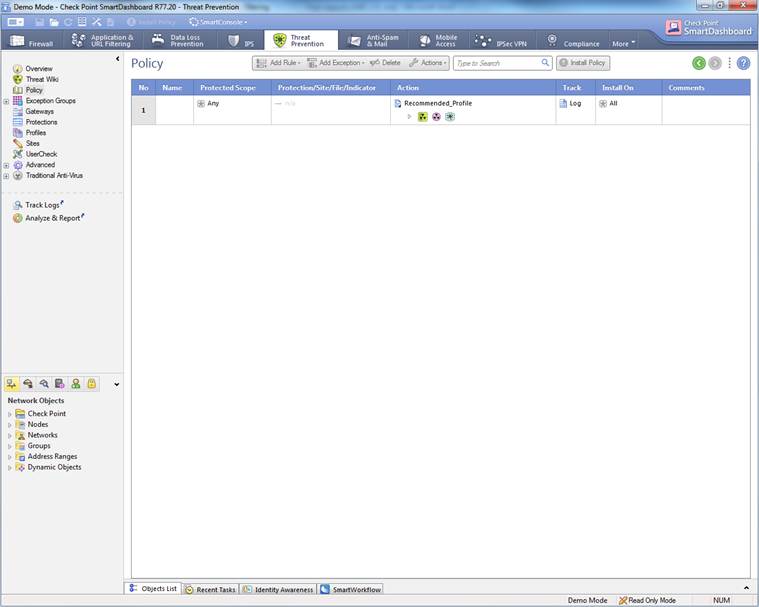
Figure. Antivirus, botnet protection and advanced threat protection rule.
Protection settings specified by the manufacturer select Threat Prevention -> Protections.
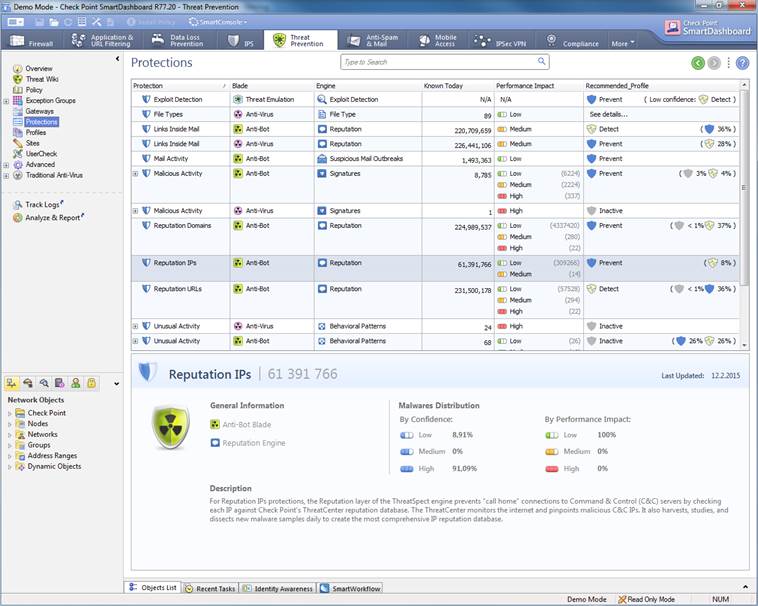 Figure. Protection settings specified by the
manufacturer
Figure. Protection settings specified by the
manufacturer
4.1 Antivirus, botnet protection and
advanced threat protection rule
In the following, you will find a picture of the antivirus, botnet protection and advanced threat protection rule and descriptions of the settings.

Figure: Antivirus, botnet protection and advanced threat protection rule
Rule number (No.)
The rule number specifies the point in the botnet prevention rule base where the rule is read.
Rule name (Name)
The name will remain unchanged in the rule base. The name can include up to 30 characters.
Protected scope
Specify what IP addresses, IP networks or users are scanned (‘Any’ refers to all).
Action
Specify the profile to be used in the rule. Instructions on how to specify the profile here.
Track
Specify whether the rule is to be tracked or not.
Comment
The comment is a free text attached to a rule.
4.2 Antivirus, botnet protection and advanced threat protection profile
Profile scanning is based on the confidence level and performance settings that are specified by the manufacturer and that can be changed.
The Antivirus, botnet protection and advanced threat protection profile can be seen select Threat Prevention ->Profile.
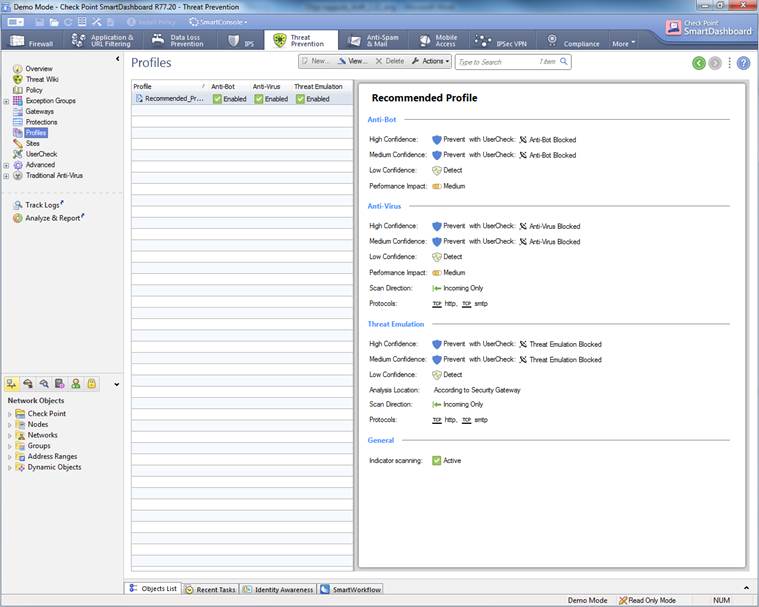
Figure: Antivirus, botnet protection and advanced threat protection profile.
In the following, you will find a picture of a profile scan activated when the service is introduced and descriptions of the settings that can be made in the fields.
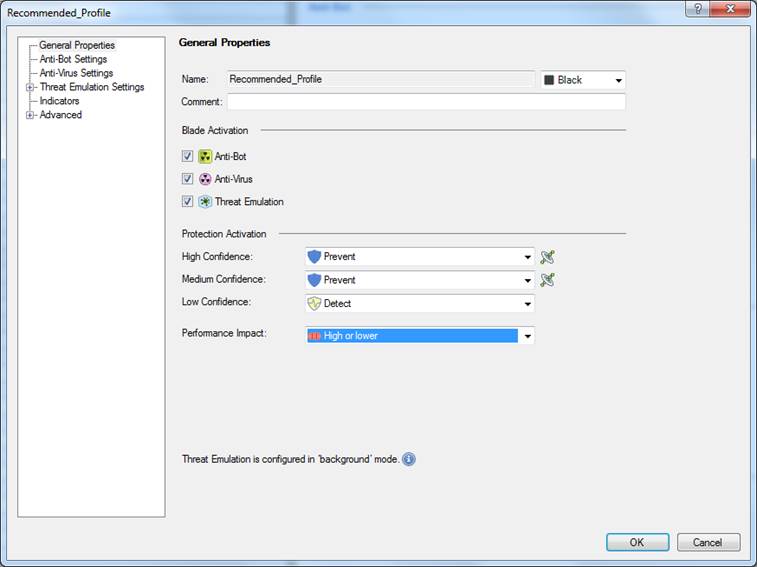
Figure: Antivirus, botnet protection and advanced threat protection profile settings.
Profile name (Name)
Profile name can include up to 60 characters.
Comment
Profile comment can include up to 80 characters.
High Confidence
The confidence level determines how likely the detected threat is actually a threat. Specify the actions to be taken with high-confidence traffic. The options are: Prevent, Detect, Ask or Inactive. The user message sent to the user is determined by these definitions. If Prevent is selected, a Block message is sent, and if Ask is selected, an Ask message is sent. The user message specifying here.
Medium Confidence
Specify what actions are to be taken with medium-confidence traffic. The options are: Prevent, Detect, Ask or Inactive.
Low Confidence
Specify the actions to be taken with low-confidence traffic. The options are: Prevent, Detect, Ask or Inactive.
Performance Impact
Specify the performance level on or below which scanning is performed. The options are: Low, Medium or lower, High or lower.
4.3 Antivirus, botnet protection and advanced threat protection user
message
User messages makes possible to be informed in real time of detected threat.
The Antivirus, botnet protection and advanced threat protection profile can be seen select Threat Prevention ->UserCheck. Message content can see in browser to select “Preview in browser”
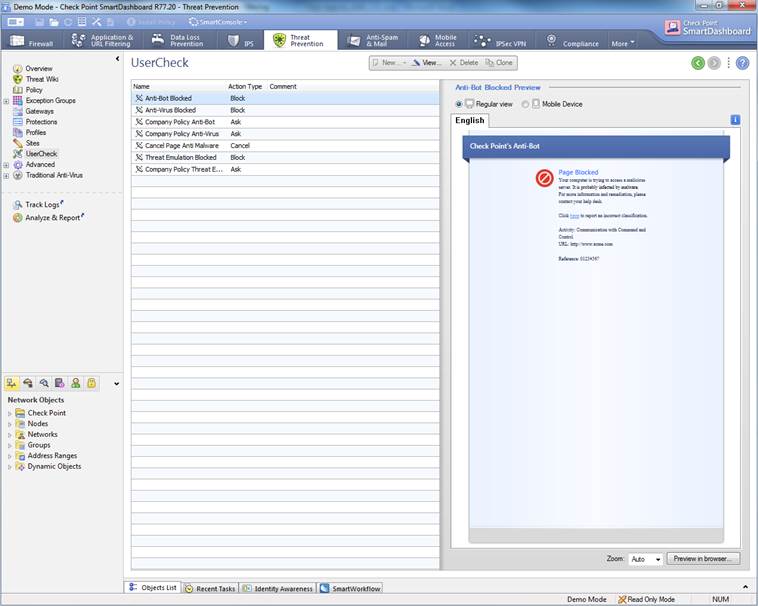
Figure. User message view.
In the following, you will find a picture of a botnet protection user message (Prevent) and how it is shown in the browser, and also descriptions of the settings that can be made in the fields.
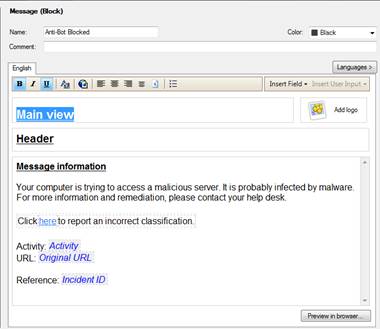
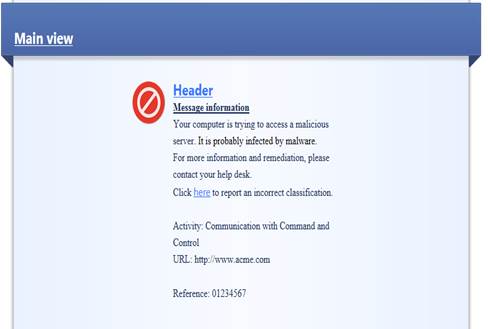
Figure: User message.
Message type (Block/Ask)
The message can be a block or an ask message. A block message is sent if the setting Prevent is selected in the profile. An ask message is sent if the setting Ask is selected in the profile.
Message name (Name)
Specify a name for the message. The name is not shown in the user message.
Message comment (Comment)
Specify a comment for the message. The comment is not shown in the user message.
User message main view (Main view)
Specify the main view (main heading) to be shown on top of the user message.
User message logo
Specify the logo to be shown in the user messages.
User message header (Header)
Specify a header for the user message information field.
User message information (Message information)
Specify the contents of the user message.
Return change targets table
5 Intrusion prevention
The intrusion prevention functionality allows the security device to detect any intrusion and attack attempts in the connections passing through it.
The intrusion prevention functionality detects, for example, network worms, Trojans, applications sending usage data without authorization (spyware), and targeted attacks towards vulnerable applications.
The intrusion prevention can be seen select IPS view.
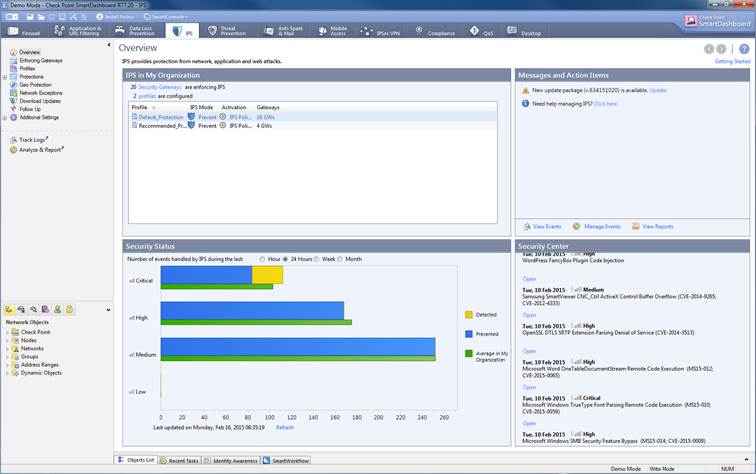
Figure: Intrusion prevention overview.
5.1 Intrusion prevention profile
The intrusion prevention profile can be seen select IPS ->Profiles
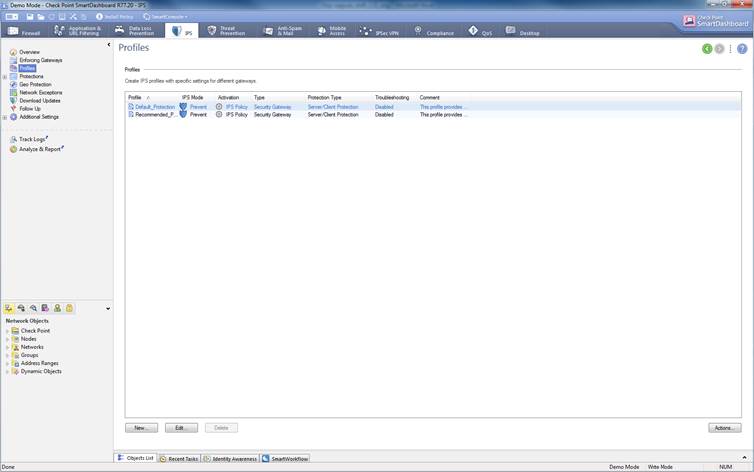 Figure: Intrusion prevention
profiles.
Figure: Intrusion prevention
profiles.
In the following, you will find a picture of a profile scan activated when the service is introduced and descriptions of the settings that can be made in the fields.
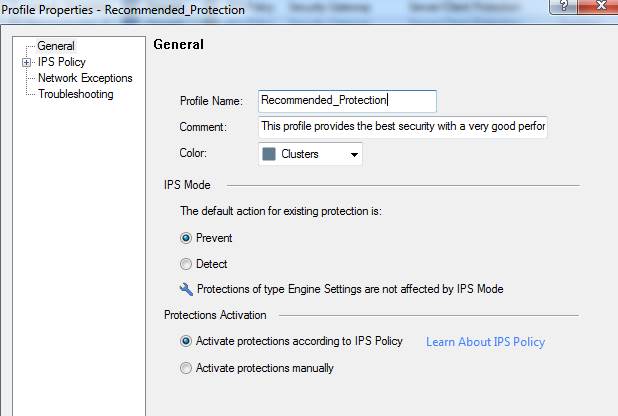
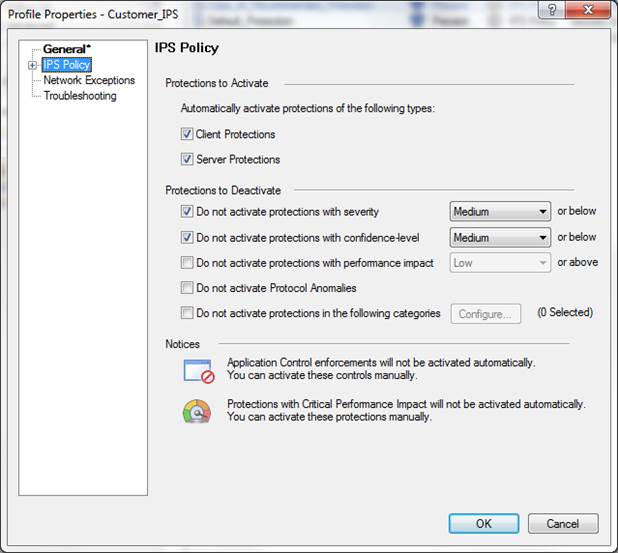
Figure: Intrusion prevention profile scans.
Profile name
Specify the profile name. The name can include up to 60 characters.
Comment
Profile comment can include up to 80 characters.
IPS settings (IPS Mode)
Specify whether intrusion/attack attempt traffic is to be prevented or detected.
Specifying the IPS policy:
Protections to activate
Specify whether scanning is activated for clients and servers.
Protections to deactivate:
Do not activate protections with severity
Specify the severity level below which scanning is not performed. The severity levels have been specified by the manufacturer. The available options are: low, medium, high, critical.
Do not activate protections with confidence level
Specify the confidence level below which scanning is not performed. The severity levels have been specified by the manufacturer. The available options are: low, medium-low, medium, medium-high, high.
Do not activate protections with performance impact
Specify the performance level above which scanning is not performed. The severity levels have been specified by the manufacturer. The available options are: very-low, low, medium, high.
5.2 Intrusion prevention
geographical protection
Geographical protection makes possible to permit or deny network traffic to or from a specific country.
The intrusion prevention geographical protection can be seen select IPS-> Geo Protection
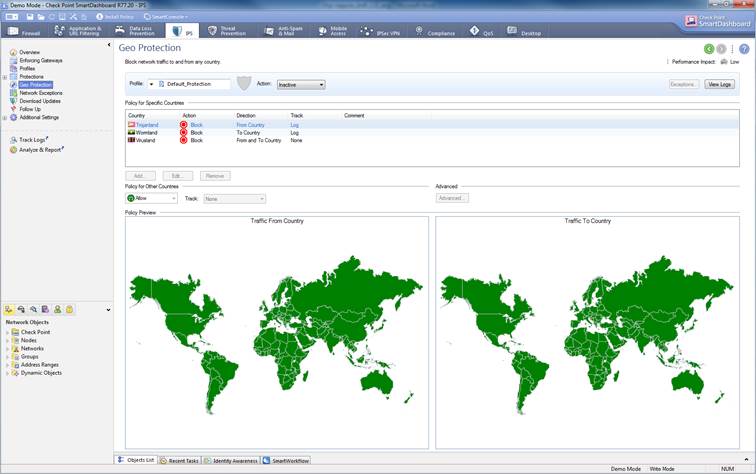
Figure. Geographical protection view.
Geographical protection are not enabled a default, settings option are detect, prevent or inactive.
In the following, you will find a picture of a geographical protection and descriptions of the settings that can be made in the fields. Settings are possible to define only detect or prevent profiles.
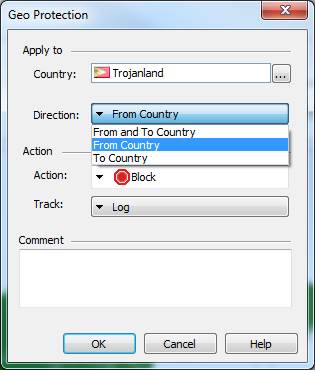
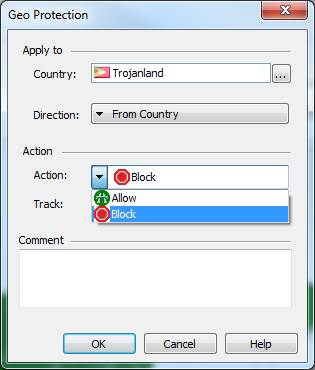
Figure. Geographical protection settings.
Country
Specify a country from or to network traffic to be permit or deny.
Direction
Specify a direction from (From Country), to (To Country), or both (From and to) a network traffic to be permit or deny.
Action
Specify whether the network traffic to permit (Allow) or deny (Block).
Track
Specify whether the rule in question is to be tracked.
Return change targets table